What is Structured Data
Structured data is data that is organized into specific data types and therefore is easily searchable and categorized. Here’s a simple example of structured data:
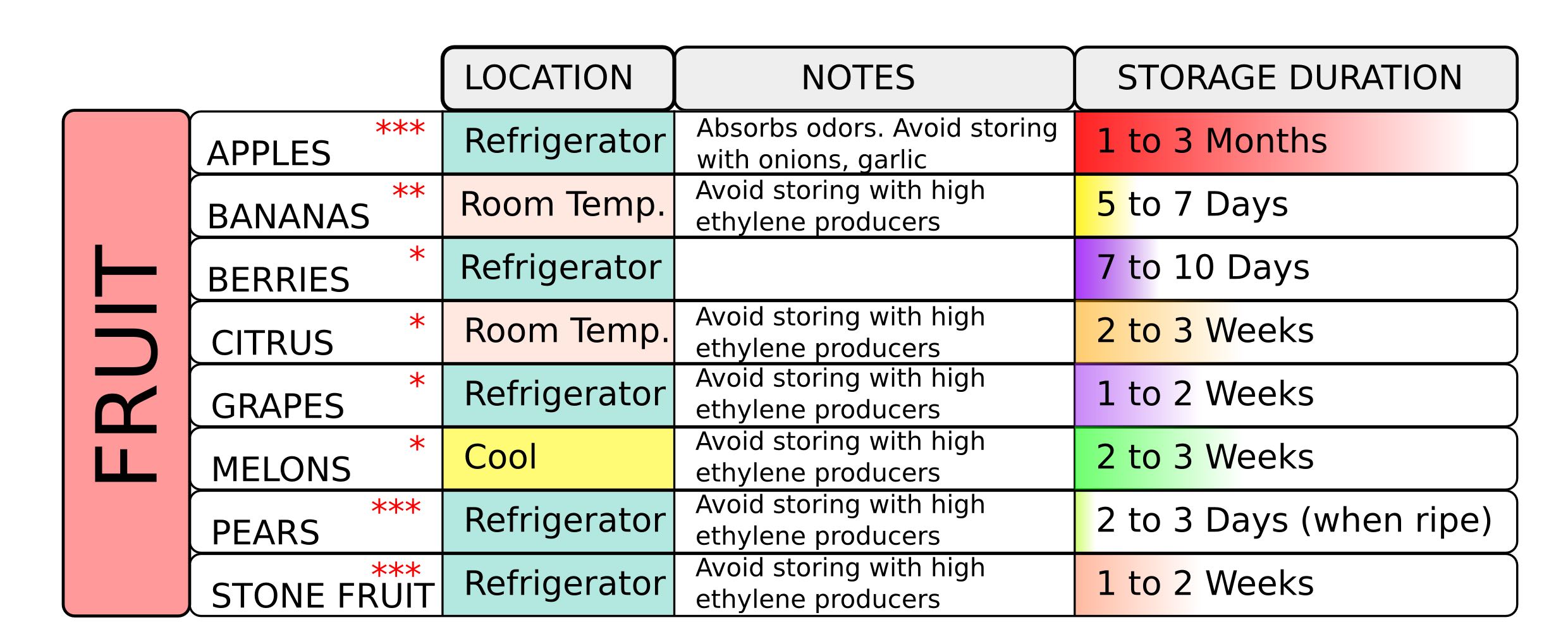
What is the Difference Between Structured Data and Unstructured Data
Unstructured data is data that is not organized in a model, schema or group. Any data, such as the below, that does not have structure is therefore unstructured:
“Bananas should be stored at room temperature and will last 5 to 7 days before spoiling
Advantages of Structured Data
Google, Facebook, Twitter, and other search engines use structured data in various formats to better understand your content. The more information you provide about your content, the better they can understand it, and the more likely that it will rank broadley for those topics.
Additionally, Google uses structured data (microdata) to display enhanced search results, such as “rich snippets”:

Here’s a few example of rich snippets for various types of content
- Events – dates and location
- Music – lyrics and track
- People – contact information
- Organizations – location and reviews
- Recipes – rating, photo, and time required
- Video – image and rating
- Products – ratings, picture and price
Structured data markup
Structured data is used to describe content on a website. Structured data markup is used to describe that content. There are various types of structured data markup, the most most common is microdata. Schema.org is an agreed upon standard of microdata that has been adopted by Google and the other search engines to better understand the web.
It looks like this:

There are hundreds of Schema.org declarations, here are some of the most popular for search:
| Schema Name | URL |
|---|---|
| Article | Schema.org/Article |
| Organization | Schema.org/Organization |
| Video | Schema.org/VideoObject |
| Author | Schema.org/Author |
| Images | Schema.org/ImageObject |
| Review | Schema.org/Review |
| Aggregate Rating | Schema.org/AggregateRating |
| Recipes | Schema.org/Recipe |
| Movies | Schema.org/Movie |
| TV | Schema.org/TVSeries |
Structured Data for Google
There are three different ways to markup data on your site for Google:
- Microdata: Uses HTML tags inline in the body of the page
- RDFa: Uses HTML tags inline in body, and tags in the head
- JSON-LD: A JavaScript notation in head or body. This is Google’s recommended method.
You should always test and review your structured data markup to ensure proper implementation. Once a page has been marked-up and pushed live, use the following:
- Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool
- Google Search Console structured data error report
Structured data is critical tool in the SEO’s belt to better help Google understand your content, and improve click through rates by generating rich snippets in the search results. Stay tuned for more 5-minute guides on structured data.
Further Reading
Need more than a Five-minute Fix? Dive deeper:

![Structured Data for SEO [5-min Guide]](https://timresnik.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/09/SocialNetworkAnalysis-1080x675.png)